Publish Date: 25 November 2025
Best treatment for arthritis in lower back involves a long-term, structured, and personalized plan that reduces pain, enhances mobility, and slows down spinal degeneration. While arthritis is a chronic and progressive condition, the right combination of physical therapy, exercise, lifestyle modifications, medications, and advanced medical treatments can dramatically improve quality of life. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of arthritis in lower back helps patients choose more effective treatments and maintain an active lifestyle.

Arthritis-related lumbar pain can affect people of all ages, though it is most common among middle-aged and older adults. Patients often describe difficulties in performing daily activities such as bending, standing, or walking for long periods. Fortunately, many conservative treatment options can successfully manage symptoms without needing surgery. The key is early diagnosis and commitment to a holistic treatment plan.
Understanding Arthritis in the Lower Back
What Is Arthritis in the Lower Back?
Arthritis in lower back refers to the degeneration or inflammation of the facet joints—the bony structures that connect the vertebrae. These joints allow spinal motion, but when the cartilage between them wears down, movement becomes painful and stiff. Over time, the body may develop bone spurs, further restricting motion and causing irritation to surrounding tissues.
This condition differs from disc herniation, although both can coexist. Arthritis usually causes mechanical pain that worsens with activity involving twisting or arching the back. Unlike some sudden painful conditions, arthritis develops gradually over years. Understanding this progression helps patients recognize symptoms earlier and adopt preventive measures before the condition worsens.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
The most significant risk factor is age-related joint wear. However, lifestyle factors like poor posture, sedentary living, repetitive lifting, and weak core muscles also contribute to early degenerative changes. Excess weight increases pressure on the lumbar spine, accelerating cartilage breakdown.
Genetics may influence the likelihood of developing degenerative joint disease. Those with a family history of osteoarthritis are more prone to experiencing similar joint deterioration. Past trauma, such as car accidents or sports injuries, can also lead to early-onset lumbar arthritis. Additionally, inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis may cause chronic inflammation in the lower spine, leading to more rapid degeneration.
Recognizing Arthritis in Lower Back Symptoms
Early Signs and Typical Symptoms
Arthritis in lower back symptoms often begin with mild, intermittent stiffness, especially in the morning or after long periods of inactivity. Many people describe a warm, achy sensation in the lower spine, which improves with gentle movement but worsens with heavy activity or prolonged standing.
As the condition progresses, the stiffness becomes more persistent. Bending backward or twisting may trigger sharper pain, while bending forward often feels relieving. Reduced flexibility, nighttime discomfort, and a grinding sensation during movement are also hallmark signs of lumbar arthritis.
In advanced cases, inflammation may irritate nearby nerves, causing radiating pain into the buttocks or upper thighs. This is different from sciatica, which typically travels below the knee, but can still significantly weaken mobility.
When to See a Doctor
If symptoms persist beyond two to six weeks despite rest and self-care, a medical evaluation is necessary. Seek immediate attention if you experience numbness, significant leg weakness, difficulty walking, or bowel/bladder control changes—these may indicate nerve involvement.
Consulting a doctor early ensures proper monitoring and reduces the likelihood of flare-ups. Delaying treatment can lead to chronic inflammation, loss of mobility, and structural spinal changes that are difficult to reverse.
Diagnosing Arthritis in the Lower Back
Diagnosis begins with a detailed discussion of symptoms, lifestyle habits, and medical history. A physical examination assesses posture, flexibility, and areas of tenderness. Physicians typically check whether pain worsens with certain movements, such as spinal extension, which often aggravates arthritic joints.
Imaging studies like X-rays help identify joint space narrowing, bone spurs, and alignment issues. MRI scans provide detailed information about disc health and inflammation. In cases where the pain source is unclear, doctors may perform diagnostic facet joint injections. If the injection relieves pain, it confirms the joint as the origin of discomfort.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial because several conditions—like sacroiliac joint dysfunction or degenerative disc disease—can mimic arthritis symptoms. Differentiating these conditions ensures tailored and effective treatment.
Best Treatment for Arthritis in Lower Back
Exercise and Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is the foundation of the best treatment for arthritis in lower back. A therapist focuses on strengthening the core, glutes, and spinal stabilizers to reduce pressure on arthritic joints. Improving posture and re-aligning the lumbar curve helps relieve joint strain.
Therapists may include manual therapy, stretching routines, neuromuscular re-education, and aquatic exercises. Many patients benefit from learning precise movement patterns that reduce stress during daily activities. Regular physical therapy can prevent the need for invasive procedures and significantly improve mobility even in severe cases.
Weight Management and Lifestyle Adjustments
Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for reducing lumbar joint compression. Even a small amount of weight loss can greatly decrease joint stress. Lifestyle changes may include adopting an active routine, improving sleep habits, and avoiding prolonged sitting.
Ergonomic adjustments—like lumbar-supportive chairs, raising monitor height, or using a standing desk—play a key role. Reducing repetitive bending and twisting motions also prevents irritation of arthritic joints.
Medications and Pain Relievers
NSAIDs reduce inflammation and ease discomfort. For patients who can’t use NSAIDs, acetaminophen offers pain relief without anti-inflammatory action. In more advanced cases, muscle relaxants or nerve-targeting medications may be prescribed.
Topical analgesics, such as anti-inflammatory gels, can help during flare-ups. Medications are most effective when combined with physical therapy and proper exercise routines.
Hot and Cold Therapy
Heat relaxes muscles and improves blood circulation, making morning stiffness more manageable. Cold therapy reduces acute inflammation and numbs localized pain. Many patients alternate between heat in the morning and ice after physical activity to maintain comfort throughout the day.
Injections and Surgical Option
Injections, such as corticosteroids or facet blocks, provide temporary relief by reducing inflammation in the affected joints. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) offers longer-lasting relief by disabling pain-transmitting nerves.
Surgery is reserved for severe cases involving spinal instability or nerve compression. Procedures like spinal fusion or decompression can restore function but require careful consideration and professional evaluation.
Natural and Home Remedies
Stretching and Gentle Movement
Daily stretching helps maintain spinal flexibility and prevents stiffness. Targeting muscles like the hamstrings, hip flexors, and glutes reduces pressure on the lumbar spine. Activities such as yoga, tai chi, or pilates offer gentle movement and postural benefits.
Low-impact aerobic exercises like walking, cycling, and water aerobics improve circulation and reduce inflammatory stiffness.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet and Supplement
An anti-inflammatory diet rich in omega‑3s, colorful vegetables, and whole grains supports joint health. Reducing sugar, processed foods, and saturated fats lowers systemic inflammation and decreases flare-ups.
Supplements like glucosamine, chondroitin, turmeric, and omega‑3 fish oil may provide additional benefits, though results vary among individuals.
Preventing Arthritis Progression
Posture and Ergonomic Habits
Correct posture protects the spine from unnecessary stress. Using a lumbar roll, adjusting desk height, and avoiding slouching help maintain neutral alignment. Replacing worn mattresses or chairs can also reduce daily strain.
Proper lifting techniques and taking regular breaks during long sitting sessions are crucial to prevent worsening symptoms.
Importance of Regular Exercise
Consistent exercise is one of the most powerful tools for slowing arthritis progression. Strengthening exercises support spinal alignment and flexibility, while cardio improves circulation and joint nutrition.
Even light daily activity reduces stiffness and boosts mood, creating a long-term benefit beyond physical improvement.
Living with Arthritis in the Lower Back
Living with arthritis in lower back can be challenging, but with a structured approach, many people regain control over their symptoms and maintain a fulfilling life. Building a support system—including physicians, physical therapists, and family members—helps sustain long-term progress.
Tracking symptoms, practicing daily movement, maintaining proper ergonomics, and staying consistent with treatment strategies are the cornerstones of successful long-term management. Arthritis may be chronic, but it doesn’t have to define your lifestyle.
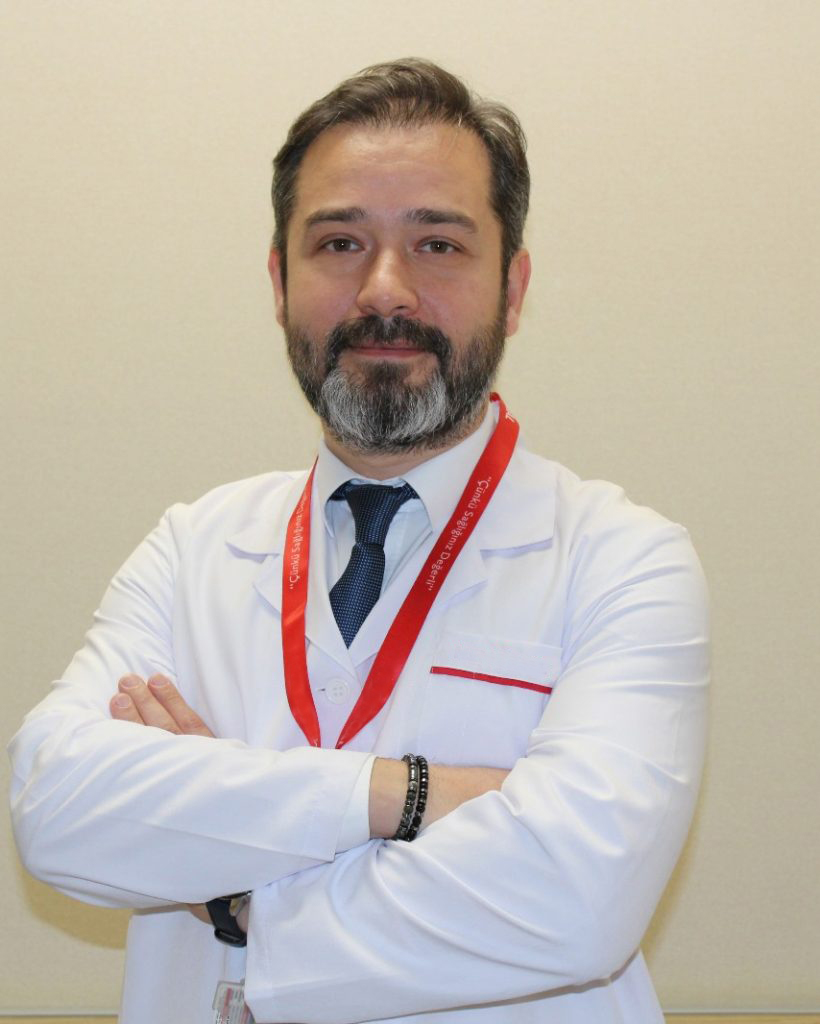

Assoc. Prof. Dr. Ömer Bozduman completed his medical degree in 2008 and subsequently served in various emergency medical units before finishing his Orthopedics and Traumatology residency in 2016. After working at Afyonkarahisar State Hospital, Tokat Gaziosmanpaşa University, and Samsun University, he continued his career at Memorial Antalya Hospital. He now provides medical services at his private clinic in Samsun, specializing in spine surgery, arthroplasty, arthroscopy, and orthopedic trauma.